Cuvis Robot: Pioneering Precision in Joint Replacements
2023-10-26

Changing Lives: The Heartbeat of Hope
in India's Transplant Revolution
2024-01-04

Heart - Lung Transplants: The Extraordinary Tale
2024-01-04
Marengo CIMS' Historic Bloodless Heart Transplant Paves the Way for a New Era in Organ Transplantation
2024-01-04

The Lifesaving Marvel of Heart Transplants: A Journey Beyond Limits
2024-01-04

What Does An ENT Do At Your First Appointment
2024-04-18

Why Choosing the Right Nephrologist in India is Crucial for Your Kidney Health
2024-04-19
Why Regular Dental Check-ups Are Essential For a Healthy Smile
2024-04-18

Hypertension in Young Adults: Understanding the Rising Health Concern
2024-08-20
Heart Failure: Symptoms, Causes, and Common Misconceptions
2024-08-20

Heart Attack in Women: 10 Warning Signs You Can’t Afford to Ignore
2024-08-20

Heart Health Tips: Strategies
for a Stronger Heart
2024-08-20

Why Are More Young Adults
Dying of Heart Attacks?
2024-08-20

Hypertension: Understanding the Silent Killer
2024-08-20

Stress and Heart Health: The Surprising Connection
2024-08-30

How Exercise Prevents Heart Conditions?
2024-08-30

Understand Arrhythmia: The Most Common Heart Problem
2024-08-30
First Aid for Heart Attacks: How to Treat a Heart Attack Emergency
2024-08-30
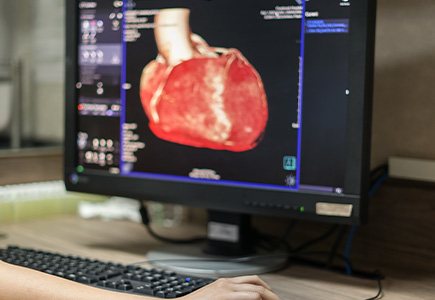
Angiography Explained: How It Helps in Heart Treatment
2024-09-16
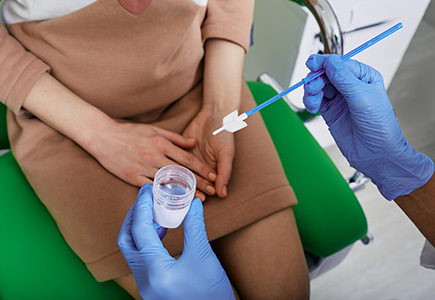
Cervical Cancer: Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
2024-09-16

Gut Microbiome and Its Impact on Digestive Health: How the gut flora influences overall well-being
2024-09-16
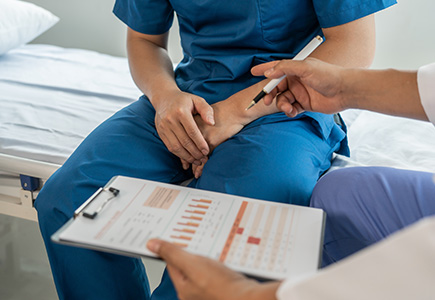
Testicular Cancer Management: Symptoms, Risk Factors and Treatment
2024-09-16
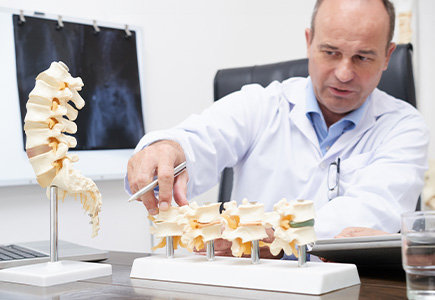
Understanding Spine Deformity: Types, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
2024-09-16
Liver Transplant: Indications, Procedure, and Recovery
2024-09-30
Debunking 10 Common Myths About Radiation Therapy
2024-09-30
The Importance of Regular Colonoscopies: Debunking myths and emphasizing early detection
2024-09-30

Exploring The Latest Advances In Cardiac Treatment
2024-09-30

Understanding Dysphoria: Causes, Symptoms, and How to Cope
2024-09-30
Understanding GERD: A Comprehensive Guide
2024-10-04
Understanding and Managing IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome): Latest treatment options and lifestyle changes
2024-10-04
8 Tips to Prevent Gastrointestinal Cancers
2024-10-11
Spinal Stenosis: Symptoms Risk Factors and Treatment Strategies
2024-10-11
The Rise of Robotic Surgery in Orthopaedics
2024-10-11
A Journey to Relief: Understanding POEM for Achalasia
2024-10-17

A Complete Guide to Understanding Bipolar Depression
2024-11-05

How Diet Impacts Mental Health?
2024-11-05

Overview of Common Respiratory Diseases: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Management Strategies
2024-11-05
Understanding Pneumothorax: A Comprehensive Guide to Collapsed Lungs
2024-11-05

Understanding Constipation: Causes, Symptoms, and Comprehensive Treatments
2024-11-19
Unlocking Relief: How Biofeedback Transformed Sarah’s Struggle with Chronic Constipation
2024-11-19
Common Misconceptions about Liposuction
2024-11-19
The Journey of Cleft Lip and Palate Surgery: From Diagnosis to Recovery
2024-11-19

Key Strategies for Supporting a Child with Autism: Coping, Advocacy, and Self-Care Tips
2024-11-22

Benefits of Breastfeeding and Methods for Mothers and Babies
2024-11-22
Understanding Ovarian Cysts: Types, Symptoms, and Diagnostic Methods
2024-11-22
7 Key Things to Steer Clear of for Optimal Kidney Health
2025-03-28

Understanding Aphasia - Symptoms, Types, Causes, and Treatment Options
2025-03-27
Key Facts About Bariatric Surgery
2025-03-26

Types of Arthritis: An Overview of Various Forms of Joint Inflammation
2025-03-28

Can a Vitamin B12 Deficiency Be a Sign of Cancer?
2025-07-15

What is the ESR Level in Cancer Patients?
2025-07-28

Warning Signs and Symptoms of a Brain Tumour
2025-09-22








