Call Us
|
MAH Faridabad 0129-6935059 |
|
MAH Gurugram 0124-4131011 |
| MCIMS Ahmedabad 079-48051904 |
| Brain Stroke Helpline Gurugram 1800-309-0247 |
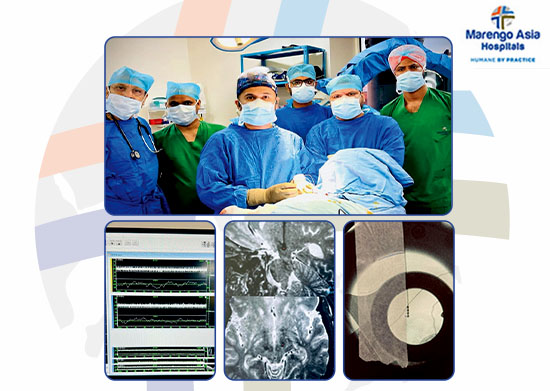
This is an interesting case about a 72-year-old Iraqi male patient with a diagnosis of Parkinson's disease for 12 continuous years. Initially, his symptoms were very well-managed with medications. However, recently his condition began to deteriorate. His symptoms, consisting of tremors, bradykinesia, and rigidity of the limbs, became accentuated in spite of continuous treatment. Moreover, he developed memory disturbances and changes in behavior on account of high doses of Parkinson's medicines.
In a case like this, where the drug therapies have little effect, DBS is one of the most effective interventions. Although there is no strict age barrier for DBS, elderly patients may face certain challenges like excessive somnolence, and disorders in movement, including dystonia. However, after a comprehensive assessment by the multidisciplinary team of Marengo Asia Hospitals, Gurugram, the patient was considered a good candidate for DBS surgery. The operation was led by Dr. Himanshu Champaneri and was a success. Astonishingly, the patient was able to walk within 24 hours of the surgery.
The procedure involved the insertion of two leads into the motor area of the subthalamic nucleus, an extremely small but significant structure within the brain, measuring approximately 4 x 3 x 2 mm. To achieve this, sophisticated techniques were employed: high-resolution MRI imaging, stereotactic guidance, intraoperative microelectrode recordings, and microstimulation. The surgery, which took roughly seven hours, included three intraoperative CT scans to ensure proper placement of the electrodes.
The other important intervention in his DBS treatment was device programming. In this, a number of parameters are tuned: contact points, frequency, pulse width, and amplitude-all at a particular setting based on the patient's needs. Small changes might thus have large effects, and precision was important to avoid complications like double vision, paresthesia, or paralysis. This was all the more important since the target area was very close to other regions implicated in emotional behavior.
After successful programming, his symptoms improved by more than 70%, with the dramatic reduction in the tremors, improvement in gait, and less slowness. Medication was reduced to half its original dose within 15 days, and psychological and emotional disturbances disappeared. Memory also showed marked improvement, with a lesser burden of medication.
This case is a state-of-the-art capability in modern neurosurgery. Functional neurosurgical surgeries, like DBS, represent one of the most sophisticated and sensitive surgeries of today. These offer new hope and improved quality of life in patients with Parkinson's disease, dystonia, tremors, epilepsy, psychiatric disorders, and chronic pain syndromes.
Many such DBS procedures have been performed at Marengo Asia Hospitals, Gurugram, by Dr. Himanshu Champaneri for various neurological and psychiatric conditions with successful outcomes. As we raise awareness about functional neurosurgery, we believe the change in life is desirable, freeing the patient from lifelong medication and many times debilitating side effects.